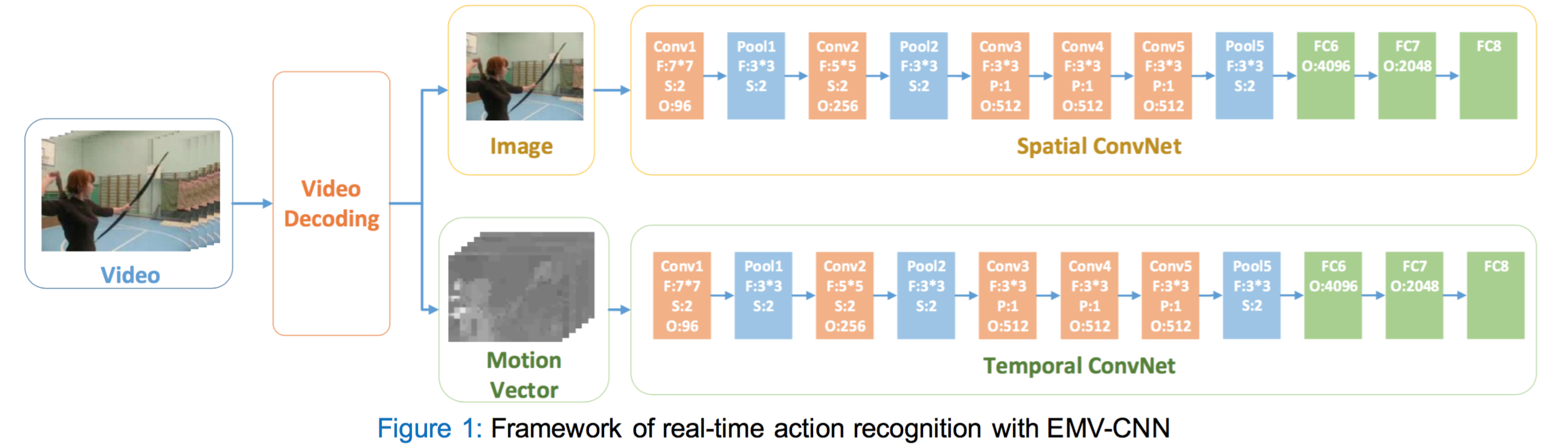
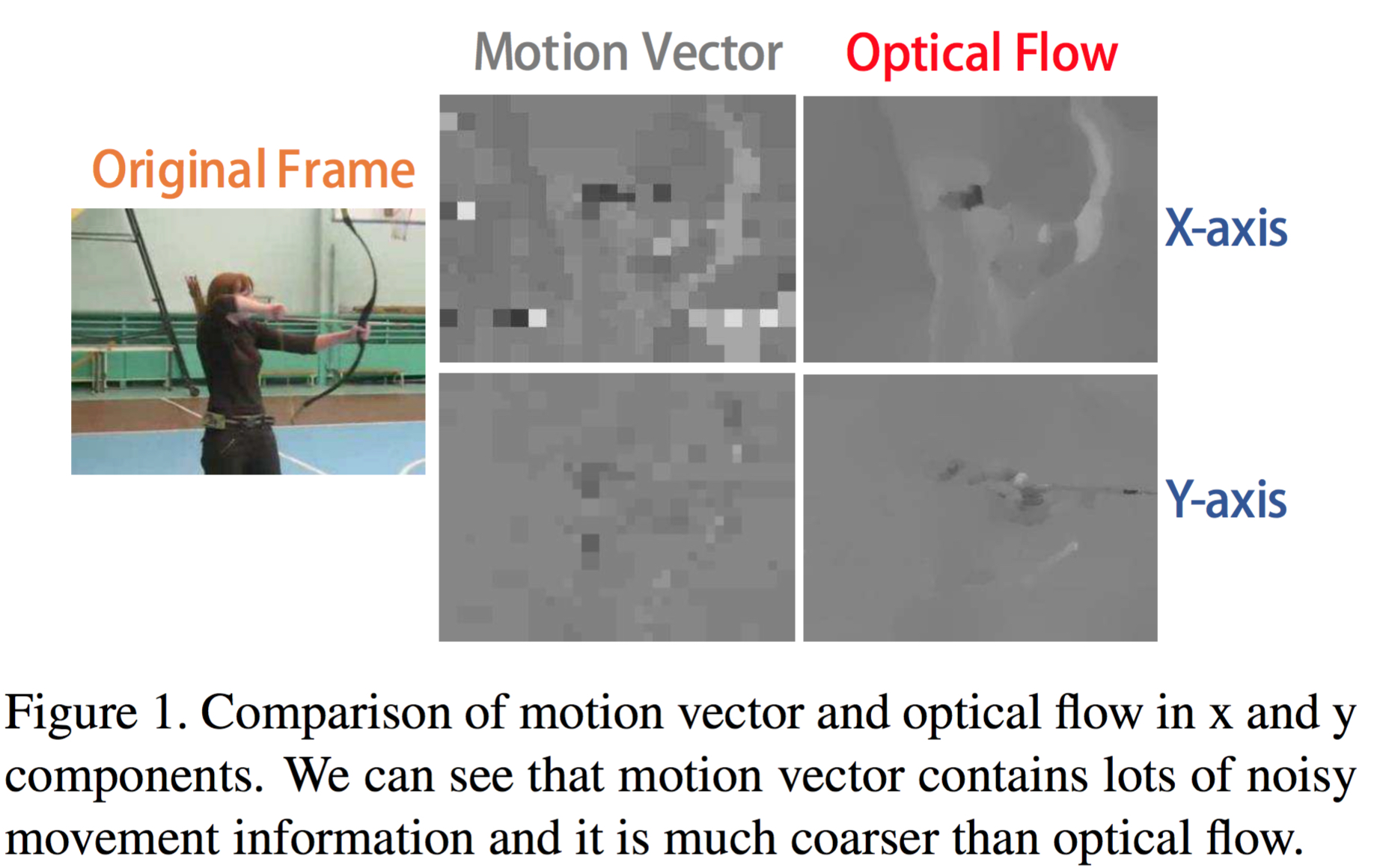
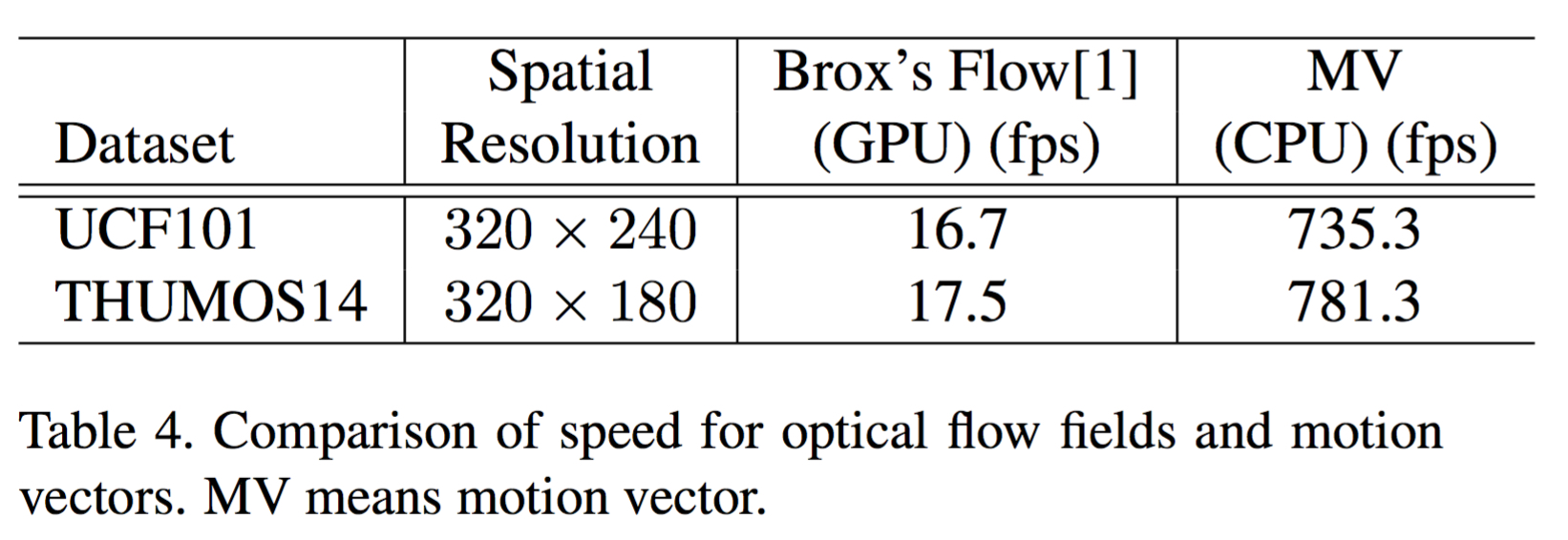
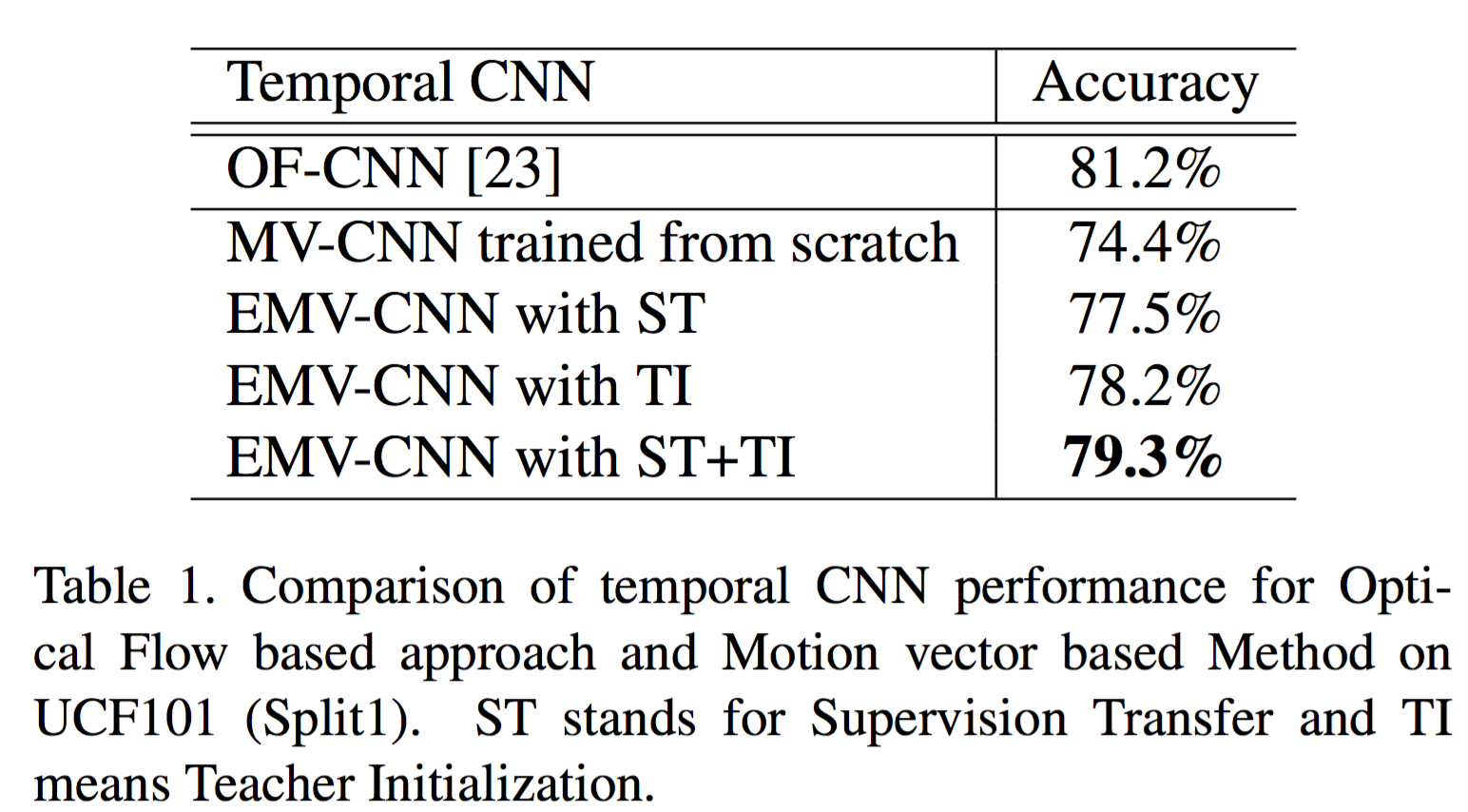
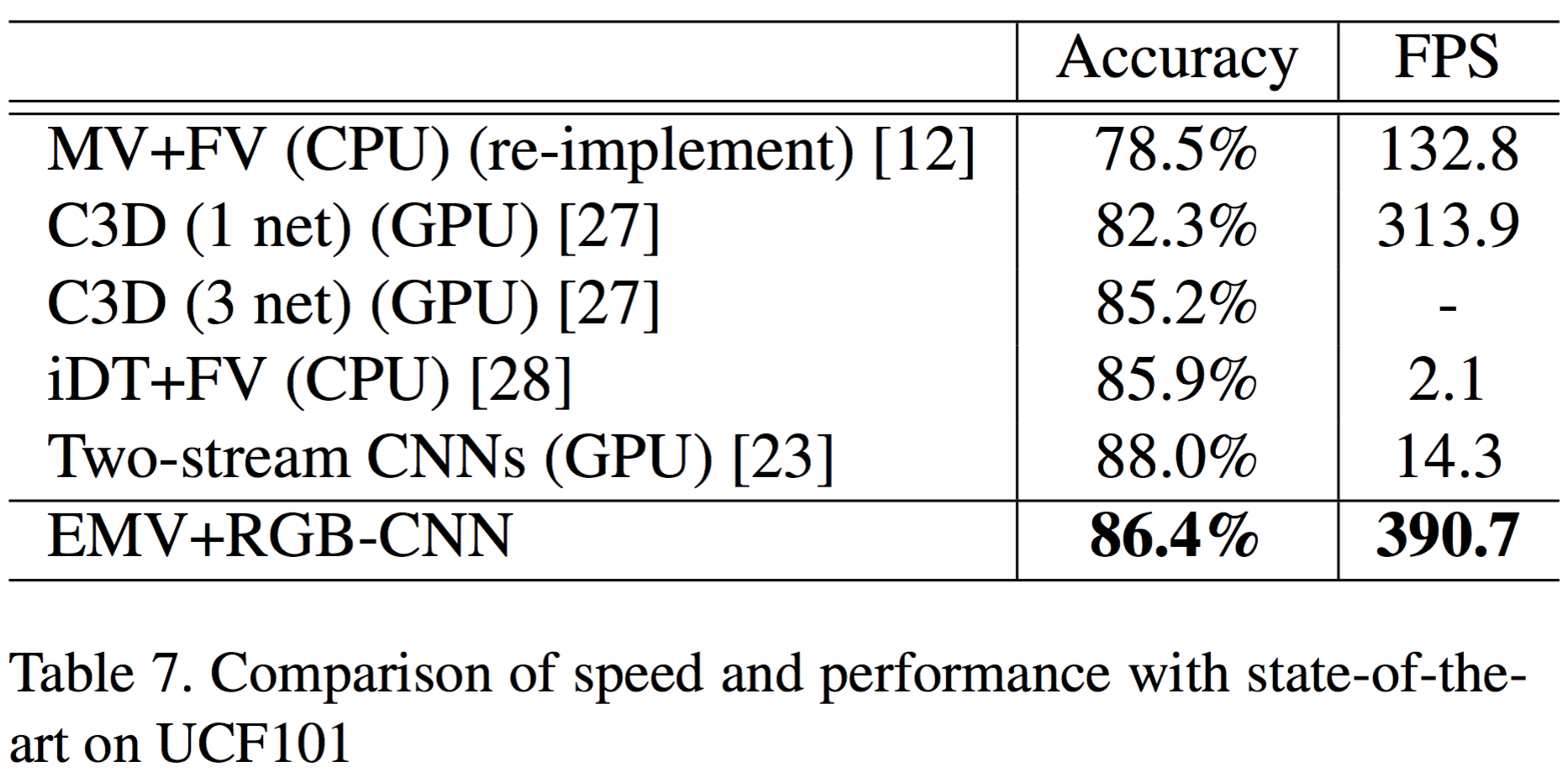
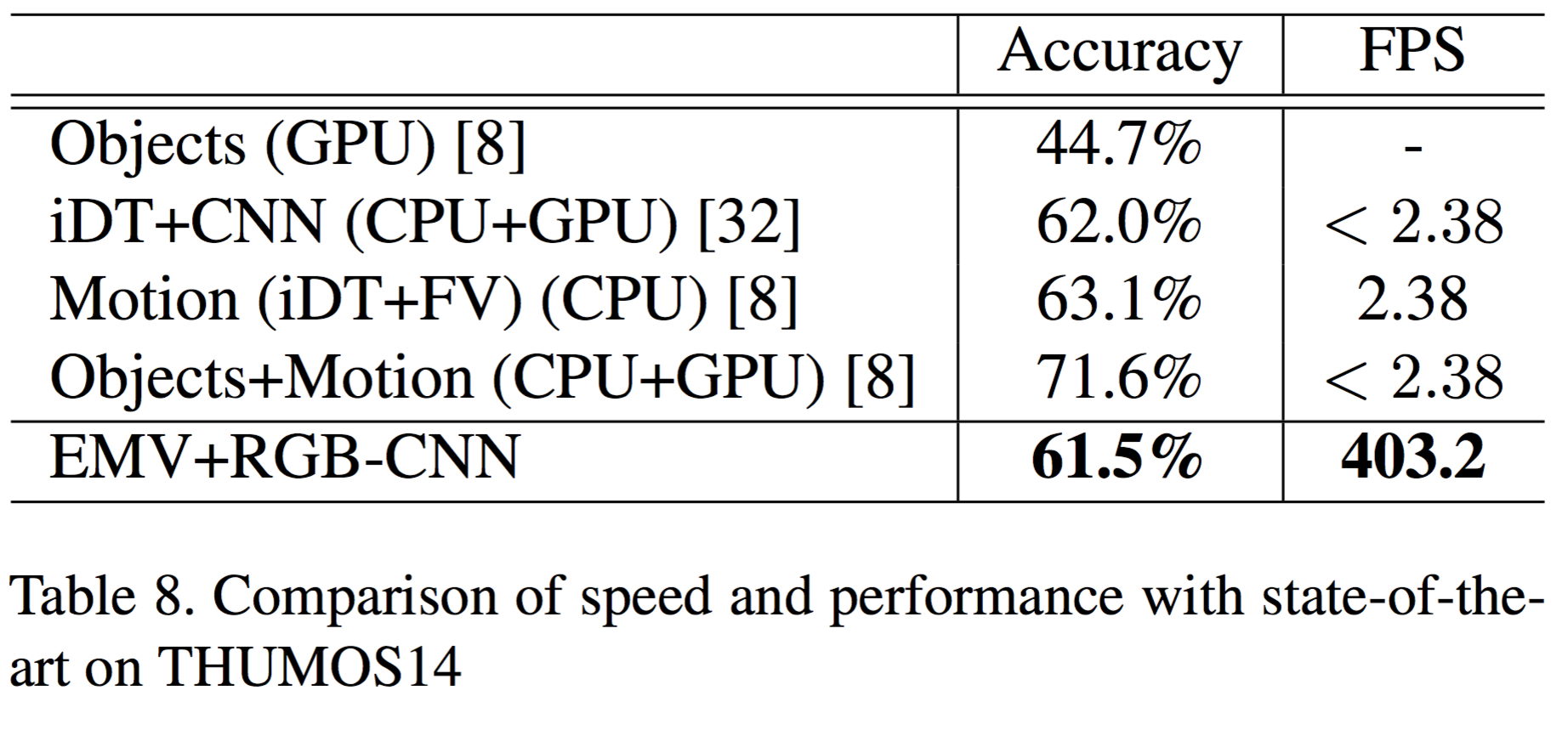
1. Using motion vector
code to generate Motion Vector Images.
2. Generating the file list for training. The list should follow this
format
3. We use the VideoData layer as input and Clarifai Net (CNN-M-2048) with PReLU to train MV-CNN.
4. For data augmentation, random crop, random filp and multi-scale (scale_ratio: [1,.875,.75]) are used.
5. Following these steps, you should get 74.4% (MV-CNN train from scratch) for UCF-101 Split1.